[모두의 딥러닝]ML lab 06-2: TensorFlow로 Fancy Softmax Classification의 구현하기
이번엔 fancy softmax classification
좀 더 이쁘게 만들어보자는 의미

주어진 X에 대해서 학습할 W을 matmul로 곱하고
이걸 logits(score)이라고 부르자
그리고 softmax를 통과시켜서 확률로 받아들이자

보면서 다시 복습해보자
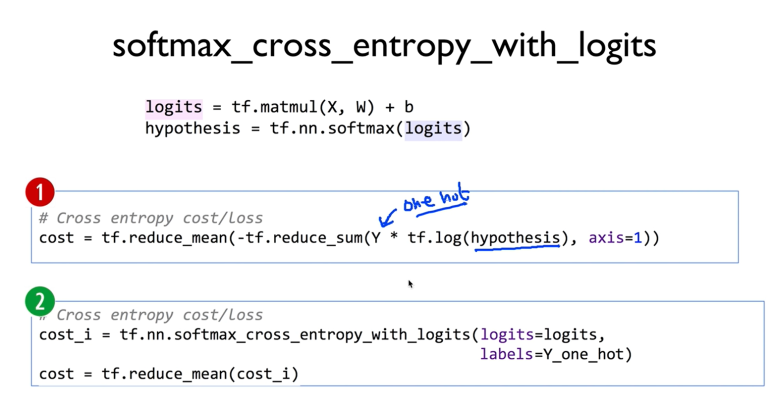
cost를 작성했다
1번을 좀 간편하게 만들고 싶다
그래서 2처럼 작성했다
이를 위해선 softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits() 라는 함수를 이용한다
이를 이용해서 cost_i를 구하고
이 cost_i의 평균을 구해서 cost에 저장한다

동물이 어떤 종인가를 예측하는 프로그램을 작성해보려고 한다
마지막 값이 0~6으로 구분이 가니까, 총 7가지 종으로 분류할 수 있을 것같다.
저 마지막 값이 Y_data 이다

Y 앞에 있는 건 X 데이터 들이다
Y값들을 one-hot으로 바꾸어 주어야한다

저 1은 한자리 라는 의미
tensorflow의 one_hot이라는 함수를 써보자
nb_classes 는 클래스의 개수이다. 여기서는 7개 이겠지
마지막 줄에 -1을 넣어준건 everything이라는 의미

전체코드이다.

argmax로 0~6사이의 값으로 만들기
session에서 학습,
x_data를 던져주고 예측한 값을 출력하도록 하기
flatten()은
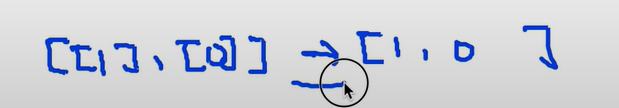
이랬던 y값을 저런식으로 바꿔준다는 의미

zip은 p와 y로 각각 넘겨주기 위함
그리고 prediction(예측한 값)과 Y(실제 값) 을 프린트 해보자
다음은 내가 colab에서 실습한 코드
구글 드라이브 마운트를 통해서 데이터를 불러왔다.
path = ' 경로 '
xy = np.loadtt(path, ~~~
로 해도 상관없고
다음과 같이 해도 상관없다
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
import numpy as np
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
xy = np.loadtxt('/content/drive/MyDrive/data-04-zoo.csv', delimiter=',', dtype=np.float32)
x_data = xy[:, 0:-1]
y_data = xy[:, [-1]]
print(x_data.shape, y_data.shape)
'''
(101, 16) (101, 1)
'''
nb_classes = 7 # 0 ~ 6
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 16])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, 1]) # 0 ~ 6
Y_one_hot = tf.one_hot(Y, nb_classes) # one hot
print("one_hot:", Y_one_hot)
Y_one_hot = tf.reshape(Y_one_hot, [-1, nb_classes])
print("reshape one_hot:", Y_one_hot)
'''
one_hot: Tensor("one_hot:0", shape=(?, 1, 7), dtype=float32)
reshape one_hot: Tensor("Reshape:0", shape=(?, 7), dtype=float32)
'''
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([16, nb_classes]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([nb_classes]), name='bias')
# tf.nn.softmax computes softmax activations
# softmax = exp(logits) / reduce_sum(exp(logits), dim)
logits = tf.matmul(X, W) + b
hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
# Cross entropy cost/loss
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=logits,
labels=tf.stop_gradient([Y_one_hot])))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(cost)
prediction = tf.argmax(hypothesis, 1)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(prediction, tf.argmax(Y_one_hot, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# Launch graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(2001):
_, cost_val, acc_val = sess.run([optimizer, cost, accuracy], feed_dict={X: x_data, Y: y_data})
if step % 100 == 0:
print("Step: {:5}\tCost: {:.3f}\tAcc: {:.2%}".format(step, cost_val, acc_val))
# Let's see if we can predict
pred = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={X: x_data})
# y_data: (N,1) = flatten => (N, ) matches pred.shape
for p, y in zip(pred, y_data.flatten()):
print("[{}] Prediction: {} True Y: {}".format(p == int(y), p, int(y)))

정확도도 100%로 잘 나오고

예측값도 잘 맞춘다.
csv 데이터 파일은 나도 다운받아 사용했다